Psoriasis is a common neurogenic skin disease. This disease is not contagious and will not spread from person to person. In most cases, psoriasis becomes a chronic disease due to its latent course. Usually, the disease occurs in people under 30 years of age, but it can also occur in old age.
There may be no external symptoms, and the clinical manifestations of the disease depend on its type and stage. In most cases, psoriasis starts with bright red spots covered with dry scales, so this disease also has a name-scaly lichen.
Skin spots can be of different sizes, and some can merge into an affected area of the skin and protrude significantly above the surface.
Psoriasis will bring physical and mental discomfort to patients, and the condition will deteriorate periodically. During this period, there will be a period of relief and symptom resolution.
Skin plaques are called psoriatic plaques or papules, and most commonly they affect the elbows and knees and spread to the head and waist. Plaque can affect other parts of the body, depending on the type of disease. Treatment can last for more than one year.
Causes

Psoriasis can cause multiple causes related to various external and internal factors:
- A common cause is genetic inheritance;
- This disease may develop due to constant stress, anxiety, shock, depression and mental disorders;
- Various autoimmune diseases and immune system dysfunction create ideal conditions for the onset of diseases on the surface of the skin;
- Chronic psoriasis can also cause metabolic disorders and endocrine system dysfunction.
The type of psoriasis and its course depend on the cause of the disease.
Classification of psoriasis
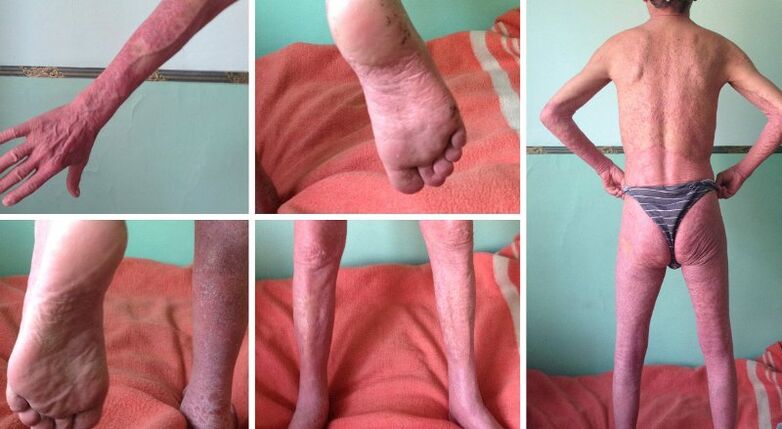
The disease has many forms, and its external manifestations and symptoms depend on:
- The most common form of this disease is squamous psoriasis. The surface of the skin is covered with red or pink patches, covered with scales. They are in sharp contrast to healthy skin, denser and bulging on the surface underneath. The scaly layer is easy to remove, and if disturbed, it will begin to bleed, which can cause severe itching and burning. When the disease worsens, the spots will grow and merge with each other, forming a large area of damage.
- Guttate psoriasis looks different, the spots can be pink or purple, and they become brighter during the worsening period. The scales can be larger and resemble water droplets in appearance; they can also merge into large areas.
- Another form of psoriasis only affects the location of the folds and skin folds-the elbows, armpits, abdomen or the area under the fat folds on the chest, the groin. The spots are smooth, uniform, not itchy, and without scales. If the affected area rubs against the clothing, the stained surface is easily injured.
- Chronic nail psoriasis is also very common, mainly affecting the nail plate on the fingers or toes. The nail loses shape, deforms, and discolors. The nails begin to thicken and fall off. This disease can cause the nail plate to fall off. Initially, nail psoriasis is easily confused with fungal infections, so you need to see a doctor for diagnosis and proper treatment.
- The most serious form of the disease is pustules, which are characterized by blisters filled with light-colored liquid, which can be easily broken by rubbing clothes. When the pustules are destroyed, the pustules will form in them, and they will infect the skin. This form of psoriasis is dangerous because it can cover almost the entire body, which can exacerbate its course.
- Rheumatoid psoriasis affects not only the skin surface, but also the joints and soft tissues around the joints. This mainly involves the knee, shoulder and hip joints. The lesion is not only manifested as external symptoms, but also as pain in the joints, which brings extra pain to the patient. If the hands or feet are affected, swelling of the fingers is observed, their sensitivity decreases and they begin to deform. In the most severe and neglected cases, patients may lose the sensitivity of their limbs and become disabled.
All these forms can progress individually or together, depending on the severity of the disease.
Stages of psoriasis
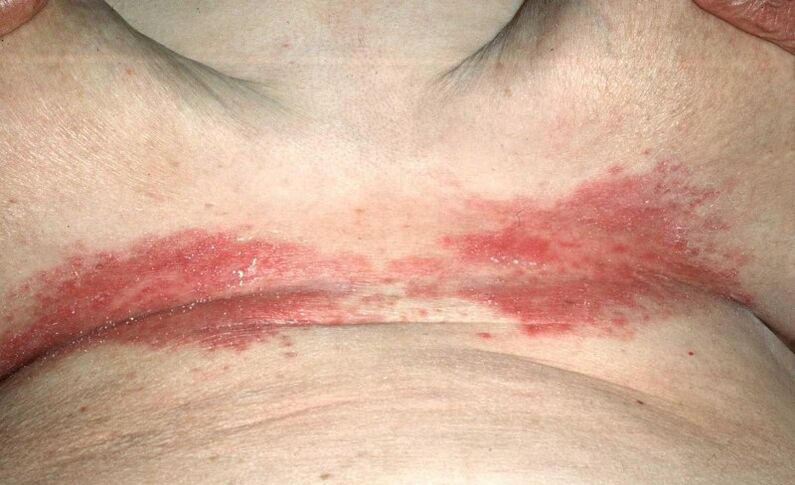
The chronic form of the disease has different stages, and each stage has its own symptoms and characteristics:
- With the gradual development, the spots covered by scales quickly appear and increase. They are usually red, but their hue can be changed according to the form of the disease. The skin in these areas is very itchy, burning, and painful;
- In the stable phase, the disease does not cause painful feelings, it flows regularly, the scales gradually grow, and they can merge periodically;
- In the regression stage, the pimples can go away on their own without causing any problems except for external symptoms.
Psoriasis is a chronic disease that alternates between worsening and remission.
Causes of aggravation

The exacerbation of this disease can be caused by many external and internal causes:
- Long-term exposure to the cold with skin frostbite;
- Violation of the body's hormonal background during puberty, pregnancy or menopause;
- Violation of dosage when taking certain drugs (antibiotics) for a long time, self-medication, taking multivitamins and herbal supplements;
- Climate change or exposure to the sun will exacerbate this disease;
- Alcoholism not only exacerbates the disease, but also complicates the course of the disease;
- Mechanical damage to the skin such as trauma, burns, frostbite, etc. will always lead to aggravation of psoriasis;
- Infection with viruses and bacteria can cause disease outbreaks, and sometimes a common respiratory disease can cause skin diseases to worsen.
Rheumatoid psoriasis has seasonal exacerbations:
- In summer-in the sun;
- In winter-due to hypothermia.
Ultraviolet rays help pimples heal, but the infrared rays of the sun can irritate the skin.
The diagnosis of psoriasis is not too difficult. The disease has obvious symptoms. In order to rule out other diseases, additional studies in the form of blood tests and skin biopsy have been carried out.
treatment
Today's medicine has made great strides in the treatment of skin diseases, including psoriasis; there are several methods that can be used to treat the advanced forms of this disease. Doctors determine treatment methods based on the form, stage, cause, and symptoms, and completely based on individual conditions. Treatment is always carried out in a comprehensive way, combining medication and physical therapy.
Medications include the use of internal and external medications:
- In order to eliminate skin diseases, ointments based on salicylic acid, sulfur, anthralin and urea are used;
- Glucocorticoid ointment;
- A lotion used to treat the scalp.
In the exacerbation stage, hormone ointment is used to eliminate the inflammatory process, and treatment always starts with weaker drugs. If the disease starts to worsen again, use a strong fluorinating agent. They are used for two weeks to achieve results.
For the elderly and children, use the ointment with the least side effects.
As the dose increases, an ointment based on anthralin is used to eliminate the inflammatory process, itching and swelling.
Prepared with kAlpotriolIt has a direct medicinal effect on pathogenic factors. It has anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. Usually, a two-month course of treatment will have obvious positive effects, and the rash on the skin may disappear completely. This remedy has no side effects in the form of skin atrophy and has a long-lasting effect. This medicine is used to treat difficult-to-treat teardrop psoriasis.
All drugs must be used alternately, otherwise addiction may occur and the body will stop responding to them.
Aromatic retinoid treatments are also considered effective.
In addition to medication, many requirements must be met for successful treatment:
- Follow the diet;
- Take the necessary vitamins under the supervision of a doctor;
- Avoid stressful situations. In the case of depression, you must consult a doctor to prescribe the necessary funds;
- Try to protect the affected area from exposure to chemicals, especially hands and nails;
- Only wear cotton clothes to avoid additional skin irritation;
- Do not drink alcoholic beverages and sweets, and avoid contact with allergens.
If all recommendations and treatment rules are followed, it is possible to achieve remission of the disease, in some cases-complete cure.























